Neoclassical Paintings
Neoclassical painting emphasized stark linear design in depictions of classical events, characters, and ideas, as well as historically accurate settings and clothing. The increased scholarly interest in ancient antiquity that evolved throughout the 18th century aided its rise significantly. The classical revival, also known as Neoclassicism, refers to artistic movements that draw influence from ancient Greece and Rome's "classical" art and culture. During the 18th century, the prominent styles were Baroque and Rococo. With its emphasis on asymmetry, vivid colours, and decoration, the latter is often regarded the polar opposite of the Neoclassical style, which is built on order, symmetry, and simplicity. Painting, sculpture, decorative arts, theatre, literature, music, and architecture all fell under the umbrella of Neoclassicism.
Classical music flourished at this time, and Jaques-Louis David's paintings became associated with the classical renaissance. Neoclassicism, on the other hand, was most powerfully felt in architecture, sculpture, and the decorative arts, where ancient models in the same medium were relatively plentiful and accessible. Sculpture, in particular, had a variety of historical models to study, but the majority were Roman reproductions of Greek originals.
Neoclassical architecture was inspired by classical architecture and, like other art forms, was a reaction against the extravagant Rococo style. In the mid-eighteenth century, the Italian architect Andrea Palladio's work became immensely prominent. Furthermore, many of the stylistic values of Neoclassical interior design based on ancient Roman rediscoveries were influenced by archeological ruins discovered in Pompeii and Herculaneum.
Neoclassical Paintings:-
The neoclassical painting was inspired by the classical art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome and was created by both men and women. The use of straight lines, a smooth paint surface hiding brushwork, the depiction of light, minimum use of colour, and the clear, crisp definition of forms are all hallmarks of Neoclassical painting. The themes mainly revolve around Greco-Roman history or other cultural concepts like allegory and virtue. Rococo painting is known for its soft paint application and lighthearted and "frivolous" subject matter, which contrasts with Neoclassical painting. Jacques-Louis David's paintings are usually regarded as the pinnacle of Neoclassical art. Several artists attempted to combine elements of Romanticism with a vaguely Neoclassical style prior to David's prominence, but their works failed to connect with customers. Neoclassical paintings frequently created by these artists also depicted historical events, mythological settings, and the architecture and ruins of ancient Rome.
The Painting School Of David:
The enormous success of David's Oath of the Horatii at the Paris Salon of 1785 gave Neoclassical painting a fresh lease on life. The painting was commissioned by the royal administration and was created in a style that combined idealised structure with dramatic effect. The painting caused a stir, and David's painting style was hailed as having perfectly articulated Neoclassical taste. As a result, he became the movement's definitive painter. The viewpoint of The Oath of the Horatii is perpendicular to the picture plane. A dark arcade stands behind numerous traditional heroic figures, defining it. The grandeur of opera is evoked by a theatrical element or staging. David quickly rose to prominence as France's leading painter, with a lot of official support. He had around 300 students in his studio throughout the course of his long career.
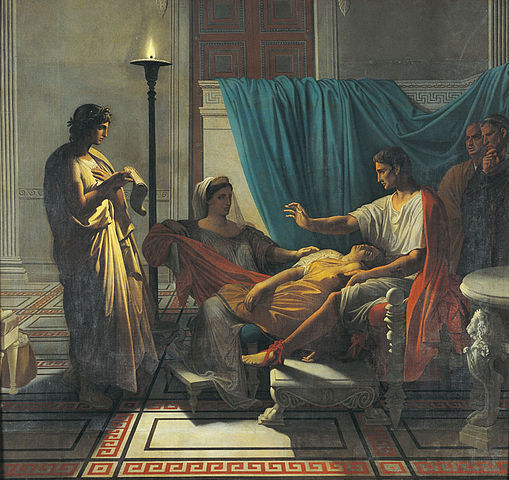
Virgil Reading to Augustus by Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres (1812): Oil on canvas
One of David's students was Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres, a Neoclassical painter of history and portraiture. Ingres was known to have regarded himself to be a conservator of the style of the ancient masters, despite the fact that he eventually painted subjects in the Romantic style. The paintings Virgil Reading to Augustus (1812) and Oedipus and the Sphinx are examples of his Neoclassical art (1864). Both David and Ingres employed the highly structured iconography, straight lines, and well defined forms that characterised Neoclassical art in the 18th century.
While tradition and the rules governing the Académie Française prohibited women from studying from the nude model (which was required for executing a successful Neoclassical painting), David believed that women were capable of producing successful Neoclassical art and welcomed many of them as his students. Marie-Guillemine Benoist, who had commissions from the Bonaparte family, and Angélique Mongez, who had patrons from as far away as Russia, were among the most successful female students of his.
In this painting, Marie-Guillemine Benoist's Self-Portrait (1788): Benoist (then Leroulx de la Ville) paints a piece from David's celebrated Neoclassical picture of Justinian's blinded general Belisarius begging for alms in this untraced oil on canvas. Her confidence as an artist and conformance to artistic trends are demonstrated by her return of the viewer's attention and her traditional dress.
After David's death in 1825, Mongez and another of David's disciples, Antoine-Jean Gros, attempted to continue the Neoclassical legacy but were unsuccessful due to the growing popularity of Romanticism. Mongez is well recognised for being one of the only women to paint gigantic subjects that sometimes contained men in their underwear, an accomplishment for which she was frequently chastised by unfriendly reviewers.
The Neoclassical movement focused on the preceding art styles of Ancient Rome and Greece. Neoclassicism was more focused on appreciating antiquity, rather than embracing it as a way of life, as the Neoclassical period often featured contemporary subjects and scenes. The primary belief from this era was that Neoclassical artwork should express ideal virtues and could therefore impart a moralizing sentiment to viewers.